
Gynecology
Ovarian Cancer Screening
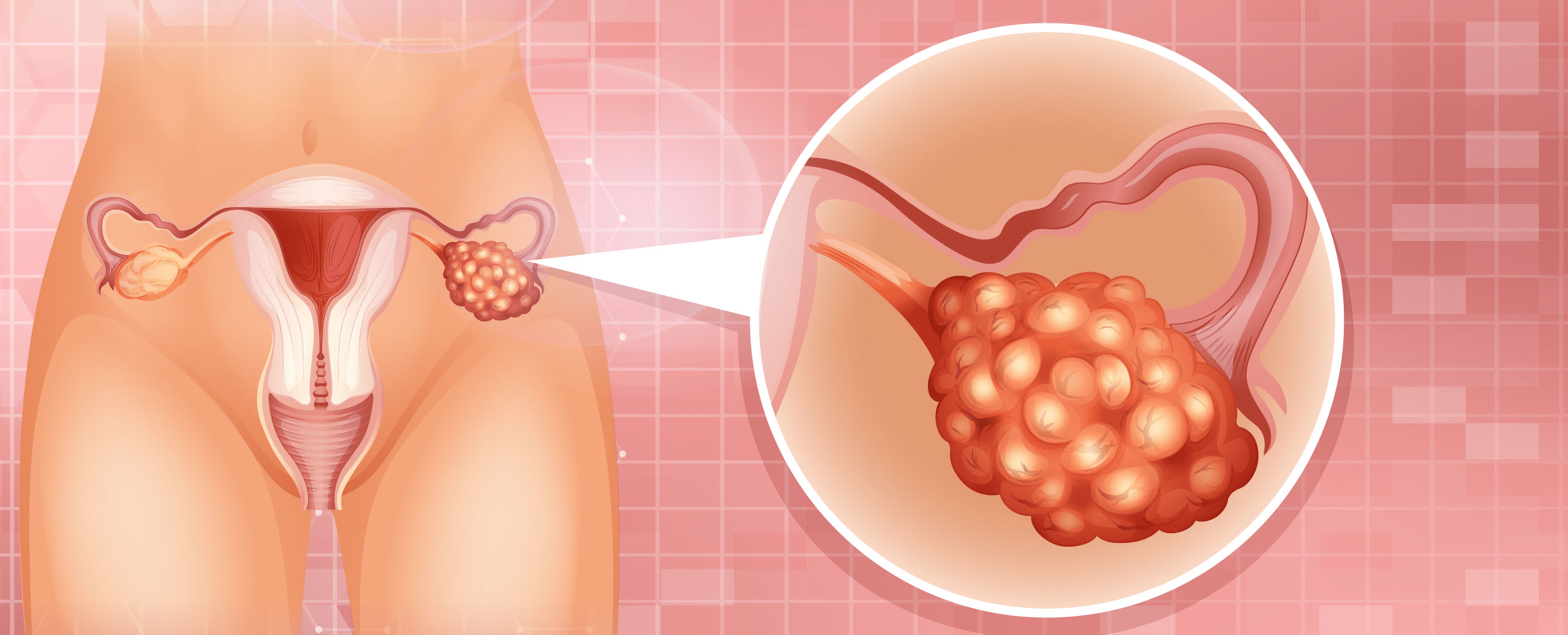
Ovarian cancer screening involves methods to detect ovarian cancer early, which can improve treatment outcomes and survival rates. Here’s a comprehensive overview of ovarian cancer screening, including symptoms, causes, procedures, and treatments:
Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
- Abdominal Bloating or Swelling: Feeling bloated or swollen, even after eating normally.
- Pelvic or Abdominal Pain: Persistent discomfort in the pelvic or abdominal area.
- Difficulty Eating or Feeling Full Quickly: Sudden changes in appetite or feeling full sooner than usual.
- Urinary Symptoms: Increased urgency or frequency of urination.
- Changes in Bowel Habits: Constipation or other changes in bowel movements.
- Fatigue: Unexplained tiredness or lack of energy.
- Back Pain: Pain in the lower back unrelated to other known causes.
Causes of Ovarian Cancer
- Age: Risk increases with age, particularly after menopause.
- Family History: Having close relatives (mother, sister, or daughter) with ovarian, breast, or colorectal cancer.
- Inherited Gene Mutations: BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations increase the risk significantly.
- Reproductive Factors: Never having been pregnant or having first pregnancy after age 35.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy: Long-term use may increase risk.
- Obesity: Higher body mass index (BMI) may be a risk factor.
- Endometriosis: A condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus.
Ovarian Cancer Screening Procedures
Currently, there is no highly effective screening test for ovarian cancer comparable to mammography for breast cancer. However, the following tests may be used in certain cases:
- Pelvic Examination: A physical exam to feel for any abnormalities in the ovaries, uterus, or nearby organs.
- Transvaginal Ultrasound (TVUS): An ultrasound probe is inserted into the vagina to create images of the ovaries and nearby structures.
- CA-125 Blood Test: Measures the level of CA-125, a tumor marker that may be elevated in ovarian cancer. It is not specific and can be elevated in other conditions.
- Genetic Testing: Testing for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations in high-risk individuals may help assess ovarian cancer risk.
Early Detection and Prevention
- Awareness of Symptoms: Understanding the signs and symptoms of ovarian cancer and seeking prompt medical evaluation for any concerning symptoms.
- Genetic Counseling: Especially for individuals with a family history of ovarian or breast cancer to assess genetic risk.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, and a balanced diet may reduce the risk of ovarian cancer.
