
Gynecology
Uterus Removal Surgery
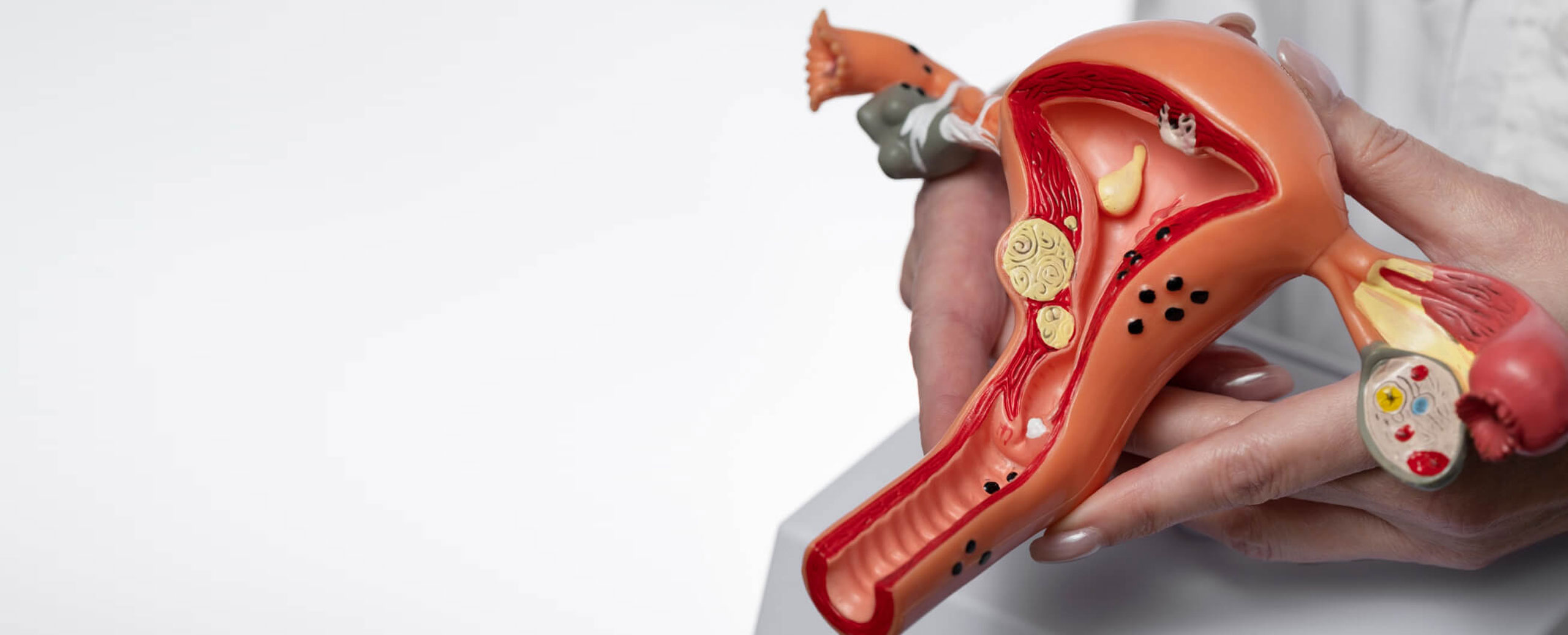
Uterus removal surgery, medically known as hysterectomy, is a procedure where the uterus is surgically removed from a woman's body. Here's a detailed overview covering symptoms, causes, procedure, and treatments related to uterus removal:
Symptoms Leading to Uterus Removal
- Heavy or Prolonged Menstrual Bleeding: Excessive bleeding that does not respond to conservative treatments.
- Uterine Fibroids: Non-cancerous growths in the uterus that cause pain, bleeding, or other complications.
- Endometriosis: A condition where the tissue lining the uterus grows outside of it, causing pain and infertility.
- Uterine Prolapse: When the uterus slips from its normal position into the vagina.
- Cancer: Uterine, cervical, or ovarian cancer affecting the uterus.
- Chronic Pelvic Pain: Persistent pain in the pelvic region that does not respond to other treatments.
Causes of Uterus Removal
- Medical Conditions: Severe cases of uterine fibroids, endometriosis, or uterine prolapse.
- Cancer: When cancer affects the uterus, cervix, or ovaries.
- Chronic Pelvic Pain: Unrelenting pain that does not respond to other treatments.
- Personal Choice: In some cases, women opt for hysterectomy for personal or medical reasons, such as preventing future health issues.
Procedure of Uterus Removal (Hysterectomy)
- Preparation: The patient is prepared for surgery with anesthesia, which may be general, regional (epidural), or local.
- Incision: A surgical incision is made in the abdomen (abdominal hysterectomy) or through the vagina (vaginal hysterectomy), depending on the reason for surgery and the patient's medical history.
- Removal: The uterus, and sometimes the cervix, is removed. In some cases, the fallopian tubes and ovaries may also be removed (salpingo-oophorectomy).
- Closure: The incisions are closed with stitches or surgical staples.
Types of Hysterectomy
- Total Hysterectomy: Removal of the uterus and cervix.
- Partial Hysterectomy (subtotal or supracervical): Removal of the upper part of the uterus, leaving the cervix intact.
- Radical Hysterectomy: Removal of the uterus, cervix, part of the vagina, and surrounding tissues (often for cancer treatment).
Recovery and Postoperative Care
- Hospital Stay: Typically 1-2 days for abdominal hysterectomy, less for vaginal hysterectomy.
- Pain Management: Pain medications are prescribed to manage discomfort.
- Activity: Rest and limited activity for several weeks, avoiding heavy lifting or strenuous activity.
- Follow-Up: Regular check-ups to monitor healing and manage any complications.
Treatment Options After Uterus Removal
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): To manage symptoms of menopause if the ovaries are removed.
- Pelvic Floor Exercises: To strengthen muscles and support pelvic organs after surgery.
- Psychological Support: Counseling or support groups to address emotional aspects of surgery.
