
Gynecology
Ovarian Cyst
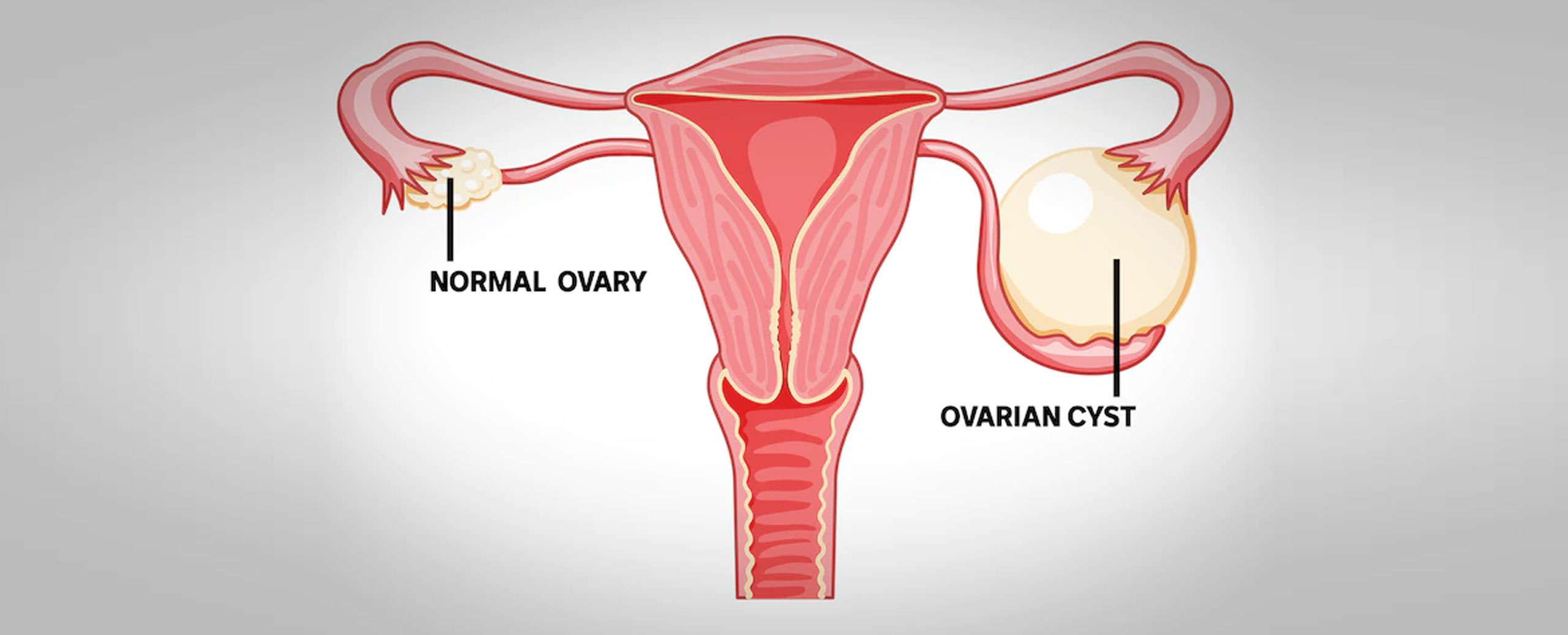
Ovarian cysts are liquid-filled sacs that develop in the ovaries. They are usually painless and have no effect on fertility when they are small, but they worsen with time. To know more about Ovarian cyst consult with our Best gynecologist for ovarian cyst in Thane, Dr. Jolly Gosavi.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can form on or inside the ovaries. In many cases, ovarian cysts do not cause symptoms and are discovered incidentally during routine pelvic examinations or imaging studies. However, when symptoms do occur, they may include:
- Pelvic Pain: Dull or sharp pain in the lower abdomen on the side of the cyst. The pain may be intermittent or constant.
- Bloating: Feeling of abdominal fullness or heaviness.
- Changes in Menstrual Cycle: Irregular periods, heavier or lighter bleeding than usual, or spotting between periods.
- Painful Intercourse: Discomfort or pain during sexual intercourse.
- Urinary Symptoms: Pressure on the bladder, causing frequent urination or difficulty emptying the bladder completely.
- Digestive Issues: Bloating, nausea, or changes in bowel habits.
Causes of Ovarian Cysts
- Follicle Cysts: The most common type, formed when an ovarian follicle fails to release an egg during ovulation or after release, the follicle closes up instead of dissolving.
- Corpus Luteum Cysts: These form when the follicle releases an egg but does not shrink after release. They usually resolve on their own but can sometimes cause pain or bleeding.
- Endometriomas: Cysts that form when endometrial tissue implants and grows within the ovary.
- Cystadenomas: These cysts develop from ovarian tissue and can become quite large.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): A condition where multiple small cysts form in the ovaries due to hormonal imbalances.
Diagnosis Procedure
If your doctor suspects an ovarian cyst based on your symptoms or during a routine pelvic examination, they may recommend the following diagnostic tests:
- Pelvic Ultrasound: This imaging test uses sound waves to create images of the ovaries and can help identify the size, location, and characteristics of the cyst.
- Pregnancy Test: To rule out pregnancy, which can sometimes cause similar symptoms.
- CA-125 Blood Test: A tumor marker test that may be elevated in certain types of ovarian cysts, although it's not specific and can be elevated in other conditions.
- MRI or CT Scan: These imaging tests may be used if the ultrasound results are unclear or if there is a need for more detailed images.
