
Gynecology
Ovarian Tumor
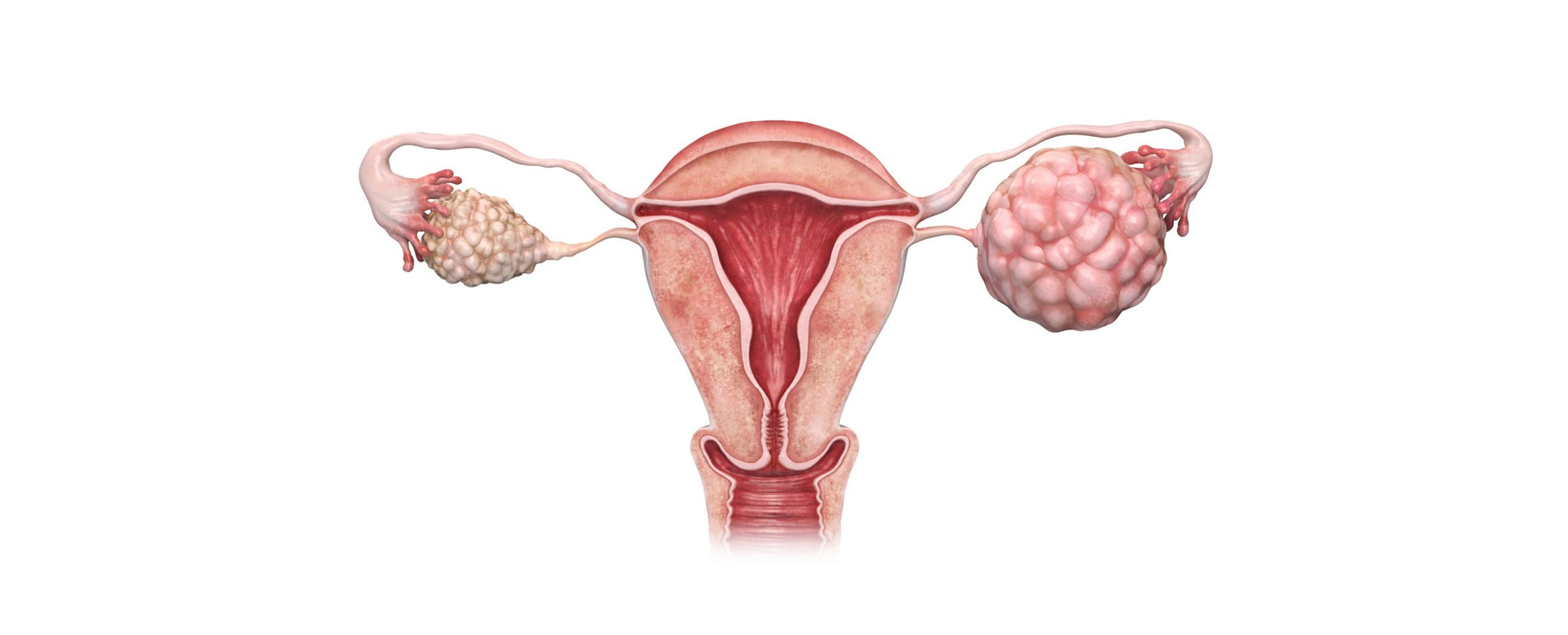
An ovarian tumor refers to an abnormal growth or mass that develops within one or both of the ovaries, which are the reproductive organs in females responsible for producing eggs and hormones like estrogen and progesterone. These tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous), and they can originate from different types of cells within the ovary.
Symptoms of Ovarian Tumors
Ovarian tumors can present with various symptoms, though they may initially be asymptomatic in many cases. When symptoms do occur, they can include:
- Abdominal Pain: Persistent or intermittent pain in the pelvic area or lower abdomen.
- Bloating: Feeling of fullness or bloating in the abdomen.
- Changes in Appetite: Loss of appetite or feeling full quickly after eating.
- Urinary Symptoms: Increased frequency or urgency of urination.
- Digestive Issues: Constipation, indigestion, or nausea.
- Menstrual Changes: Irregularities in the menstrual cycle.
- Unexplained Weight Loss or Gain: Sudden weight changes without a clear cause.
Causes of Ovarian Tumors
- Epithelial Tumors: These tumors arise from the cells that cover the surface of the ovary. They are the most common type and can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous).
- Germ Cell Tumors: These tumors develop from the cells that produce eggs within the ovary. They can also be benign or malignant.
- Sex Cord-Stromal Tumors: These tumors develop from the connective tissue cells that hold the ovary together and produce female hormones.
Treatments for Ovarian Tumors
- Surgical Removal: For most ovarian tumors, surgical removal is the primary treatment. This can involve:
Fertility-Sparing Surgery: Removing only the tumor or part of the ovary while preserving fertility.
Hysterectomy: Removing the uterus and possibly the ovaries if the tumor is large, malignant, or if there are concerns about cancer spreading.
Laparoscopic Surgery: Minimally invasive surgery performed through small incisions in the abdomen for smaller tumors or early-stage cancers. - Chemotherapy: Used to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors, especially if the tumor is malignant or has spread beyond the ovary.
- Radiation Therapy: Less commonly used for ovarian tumors, but may be recommended in specific cases to target cancer cells with high-energy rays.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs that specifically target cancer cells based on their genetic mutations or other specific characteristics.
